Enabled software revolutionizes the way businesses operate, offering innovative solutions to streamline processes and boost efficiency. Dive into the world of enabled software and discover its transformative impact across various industries.
Exploring different types, implementation strategies, and security measures, this topic delves deep into the realm of enabled software, providing valuable insights for businesses seeking to optimize their operations.
Definition of Enabled Software
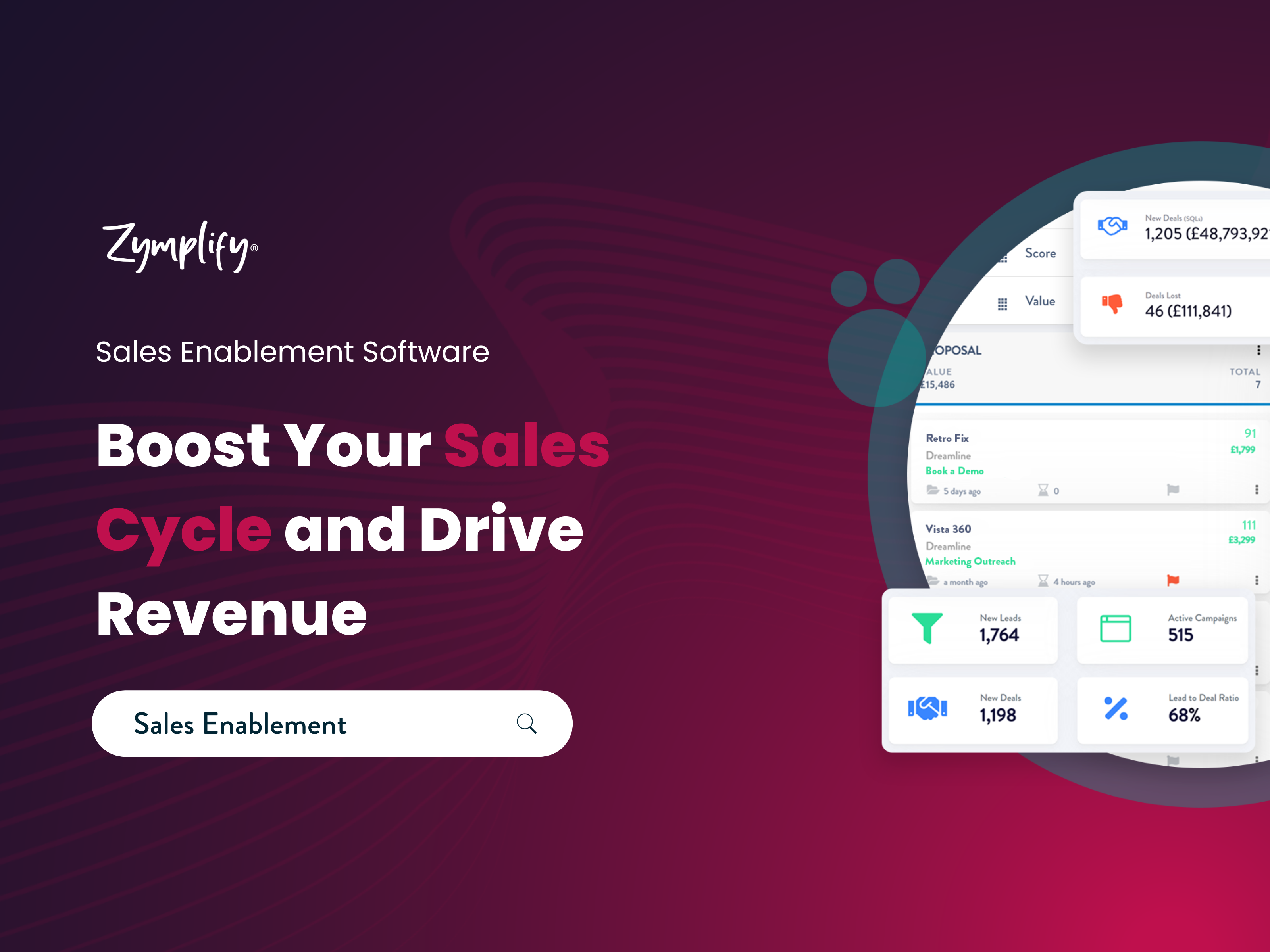
Enabled software refers to programs or applications that are designed to work seamlessly with various devices, systems, or platforms to enhance functionality and user experience.
Enabled software functions by utilizing APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to communicate and interact with different components or services, allowing for integration and interoperability across multiple technologies.
Examples of Industries/Applications
- Smart Home Automation: Enabled software enables the control of smart devices such as lights, thermostats, and security systems through a centralized platform.
- Healthcare: Electronic health record systems use enabled software to securely store and share patient information among healthcare providers.
- Retail: Point-of-sale systems utilize enabled software for inventory management, customer transactions, and data analytics.
- Manufacturing: Industrial automation systems rely on enabled software for monitoring and controlling production processes.
Benefits of Enabled Software
- Improved Efficiency: Enabled software streamlines operations by automating tasks and integrating data across different systems, reducing manual efforts and errors.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Enables seamless communication between devices, applications, and services, fostering collaboration and data sharing.
- Scalability and Flexibility: With enabled software, businesses can easily scale their operations and adapt to changing requirements without significant disruptions.
- Enhanced User Experience: Enabled software provides a cohesive and user-friendly interface, making it easier for users to interact with technology and access desired functionalities.
Types of Enabled Software

Enabled software comes in various categories, each designed to cater to specific needs and requirements. Below are some of the common types of enabled software available in the market:
1. Communication Software
- Communication software enables users to connect with others through various channels such as email, instant messaging, video conferencing, and VoIP calls.
- Features include voice and video calls, file sharing, screen sharing, and group messaging.
- Popular examples include Skype, Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom.
2. Productivity Software, Enabled software
- Productivity software helps individuals and businesses streamline tasks, manage projects, and increase efficiency.
- Features may include word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, note-taking, and project management tools.
- Well-known productivity software includes Microsoft Office, Google Workspace, Trello, and Evernote.
3. Security Software
- Security software is essential for protecting devices and data from cyber threats such as viruses, malware, and hackers.
- Features include antivirus scanning, firewall protection, encryption, and secure browsing tools.
- Popular security software includes Norton Antivirus, McAfee, Bitdefender, and Malwarebytes.
4. Multimedia Software
- Multimedia software is used for creating, editing, and sharing various types of media such as images, videos, and music.
- Features may include photo editing, video editing, graphic design, and audio mixing tools.
- Common multimedia software includes Adobe Creative Cloud, Final Cut Pro, Audacity, and VLC Media Player.
5. Accounting Software
- Accounting software is designed to help businesses manage their finances, track expenses, and generate reports.
- Features include invoicing, budgeting, payroll management, and tax preparation tools.
- Popular accounting software options are QuickBooks, Xero, FreshBooks, and Wave Financial.
Implementation of Enabled Software
Implementing enabled software in a business or organizational setting requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to integrate enabled software into existing systems and best practices to follow for a successful implementation.
Step-by-Step Guide for Integration
- Assess Current Systems: Evaluate existing systems and processes to identify areas where enabled software can be integrated for improvement.
- Set Clear Objectives: Define specific goals and objectives for implementing the enabled software to ensure alignment with business needs.
- Select the Right Software: Choose enabled software that meets the requirements of your organization and offers the features needed to achieve your objectives.
- Plan Implementation Strategy: Develop a detailed plan outlining timelines, resources, and responsibilities for the implementation process.
- Train Employees: Provide training to employees on how to use the enabled software effectively to maximize its benefits.
- Test and Validate: Conduct thorough testing of the software to identify any issues and ensure proper functionality before full deployment.
- Rollout and Monitor: Implement the enabled software in phases and closely monitor its performance to address any issues promptly.
- Collect Feedback: Gather feedback from users to make adjustments and improvements to the software as needed.
Best Practices for Smooth Transition
- Communicate Effectively: Keep all stakeholders informed about the implementation process and address any concerns or questions promptly.
- Engage End Users: Involve end users in the planning and testing phases to ensure the software meets their needs and is user-friendly.
- Provide Ongoing Support: Offer continuous support and training to users post-implementation to help them adapt to the new software.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor the performance of the enabled software and gather data to measure its impact on business operations.
- Stay Flexible: Be prepared to make adjustments and refinements to the implementation plan based on feedback and evolving business needs.
Security and Compliance with Enabled Software

When using enabled software, ensuring security measures are in place is crucial to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Compliance with regulations is also essential to avoid legal issues and maintain trust with customers.
Common Security Threats
Enabled software may face various security threats that can compromise data integrity and confidentiality. It is important to be aware of these threats and take proactive measures to mitigate them.
- Malware: Malicious software such as viruses, worms, and ransomware can infect enabled software systems, leading to data loss or theft. Regularly updating antivirus software and conducting security scans can help prevent malware attacks.
- Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals may use phishing emails or messages to trick users into revealing sensitive information like login credentials. Educating users about identifying phishing attempts and implementing email filters can reduce the risk of falling victim to such attacks.
- Data Breaches: Weak passwords, unsecured networks, and vulnerabilities in enabled software can result in data breaches. Implementing strong encryption, access controls, and regular security audits can help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Using enabled software also entails complying with various regulations to protect user privacy and ensure data security. Non-compliance can lead to legal penalties and damage to the organization’s reputation.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Companies handling data of European Union citizens must comply with GDPR requirements to protect personal data and privacy. This includes obtaining consent for data processing, implementing data protection measures, and notifying authorities of data breaches.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Healthcare organizations using enabled software must adhere to HIPAA regulations to safeguard patient information and maintain confidentiality. This involves implementing secure data storage, access controls, and regular risk assessments.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): Businesses processing credit card payments through enabled software need to follow PCI DSS guidelines to ensure secure payment transactions. This includes encrypting cardholder data, securing networks, and conducting regular security testing.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, enabled software stands as a powerful tool for enhancing productivity and ensuring seamless workflows. Embracing this technology can lead to significant improvements in business performance and overall success.
FAQ Explained: Enabled Software
How does enabled software differ from traditional software?
Enabled software is specifically designed to integrate with existing systems and provide advanced functionalities tailored to specific business needs, unlike traditional off-the-shelf software.
What are some common industries that benefit from enabled software?
Industries such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and logistics often leverage enabled software to optimize their operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation.
How can businesses ensure the security of enabled software?
Implementing robust security measures, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and staying updated on security best practices are essential steps to safeguarding enabled software from potential threats.
