Blacklisting software plays a crucial role in cybersecurity by identifying and blocking malicious content. Let’s delve into its types, working mechanisms, challenges, and best practices for implementation.
Introduction to Blacklisting Software
Blacklisting software is a cybersecurity tool used to block access to specific websites, IP addresses, or applications that are deemed harmful or malicious. Its primary purpose is to protect computer systems and networks from cyber threats by preventing users from interacting with potentially dangerous content.
Industries and Organizations Using Blacklisting Software
- Financial institutions: Banks and financial organizations use blacklisting software to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive financial data.
- Government agencies: Government entities employ blacklisting software to safeguard classified information and defend against cyber attacks.
- Corporate businesses: Companies utilize blacklisting software to protect their networks and confidential data from cyber threats.
Importance of Blacklisting Software in Cybersecurity
Blacklisting software plays a crucial role in cybersecurity by proactively blocking known threats and malicious content. By maintaining a constantly updated list of prohibited sites and applications, blacklisting software helps prevent security breaches, data theft, and malware infections. This proactive approach enhances overall network security and reduces the risk of cyber attacks.
Types of Blacklisting Software
When it comes to blacklisting software, there are various types available in the market, each with its own set of features, benefits, and limitations. Let’s explore some of the most common types and see how they compare.
1. Domain Blacklisting Software
Domain blacklisting software focuses on blocking access to specific domains or websites that are deemed harmful or inappropriate. This type of software is commonly used in schools, organizations, and homes to restrict access to certain websites.
- Features:
- Ability to block specific domains.
- Customizable blacklists based on user preferences.
- Real-time updates for new malicious domains.
- Benefits:
- Effective in blocking known malicious websites.
- Helps enforce internet usage policies.
- Limitations:
- May not be effective against unknown threats.
- Requires regular updates to maintain effectiveness.
2. Application Blacklisting Software
Application blacklisting software focuses on blocking specific applications or programs from running on a system. This type of software is commonly used in business environments to prevent the use of unauthorized or potentially harmful software.
- Features:
- Ability to block specific applications based on file hashes or signatures.
- Centralized management of blacklisted applications.
- Detailed reporting and logging of application usage.
- Benefits:
- Enhanced security by preventing the execution of unauthorized software.
- Improved productivity by limiting access to non-work-related applications.
- Limitations:
- May impact legitimate applications if not configured correctly.
- Requires regular monitoring and updates to maintain effectiveness.
How Blacklisting Software Works
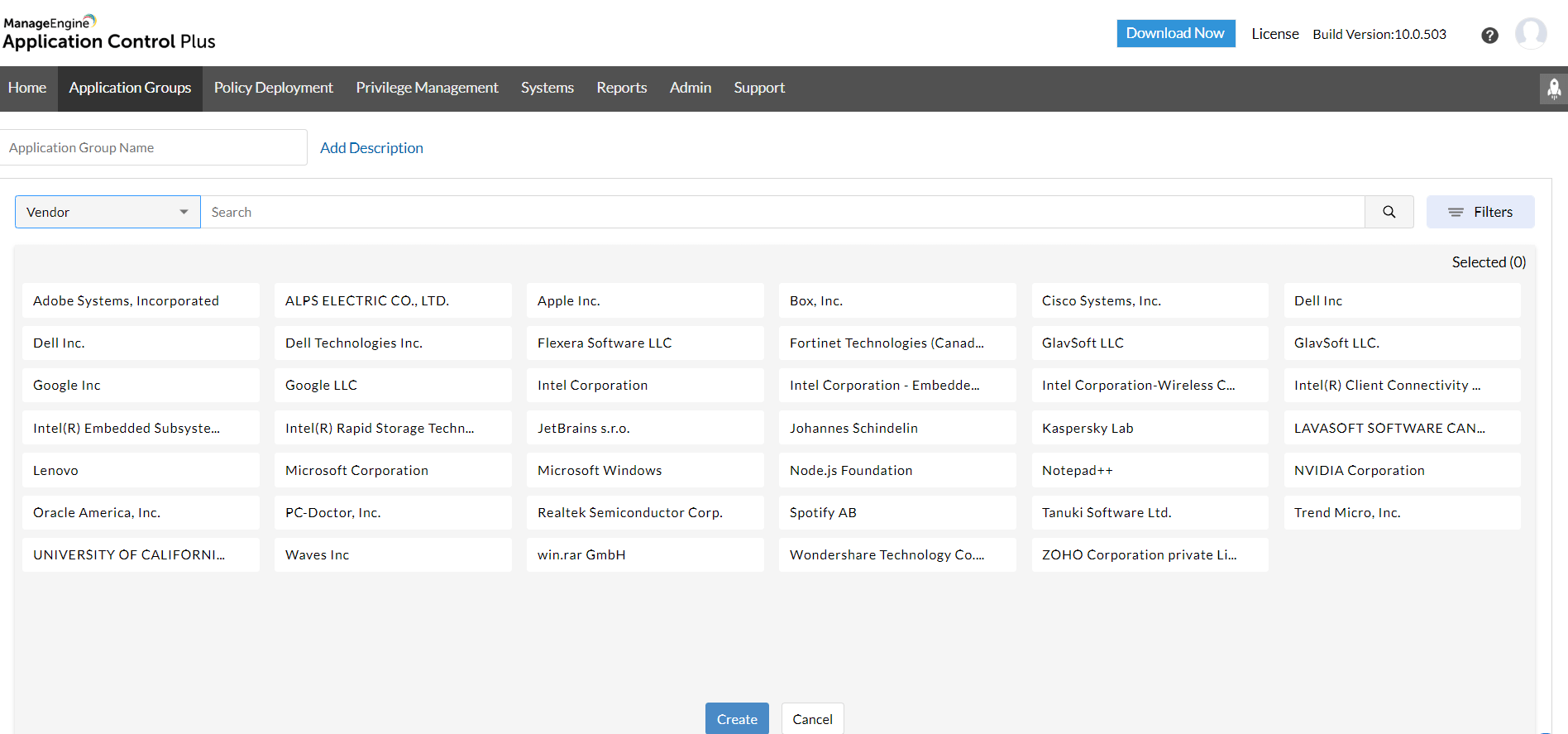
Blacklisting software works by scanning incoming data, such as websites or emails, for known malicious content based on a database of identified threats. When the software detects a match with any of the known threats, it blocks access to the content or prevents the user from interacting with it.The criteria used by blacklisting software to determine what to block include signatures of known malware, suspicious URLs, phishing attempts, and other indicators of malicious activity.
These criteria are constantly updated to stay ahead of emerging threats in real-time.
Scenarios where Blacklisting Software is Effective
- Blocking access to websites known to distribute malware or engage in phishing attacks, protecting users from potential harm.
- Preventing employees from accessing malicious links or attachments in emails, reducing the risk of a cyberattack on the organization’s network.
- Stopping the execution of files with known harmful behaviors, such as ransomware, before they can cause damage to a system.
Challenges and Limitations of Blacklisting Software

Despite their effectiveness, blacklisting software faces several challenges and limitations when it comes to blocking threats and ensuring cybersecurity.
Common Challenges Faced by Blacklisting Software
One of the main challenges faced by blacklisting software is the constant need to update the blacklist database to keep up with new threats. Cybercriminals are always finding new ways to bypass blacklists, making it a never-ending battle for cybersecurity professionals.
Another challenge is the high rate of false positives, where legitimate websites or applications are mistakenly blocked due to being incorrectly identified as threats. This can lead to disruptions in normal business operations and user experience.
Limitations of Blacklisting Software Compared to Other Cybersecurity Measures
While blacklisting software is effective in blocking known threats, it falls short when it comes to dealing with zero-day attacks, which are new and previously unknown vulnerabilities that have not yet been added to the blacklist database. This leaves systems vulnerable until the threat is identified and added to the blacklist.
Additionally, blacklisting software relies on reactive measures to block threats, meaning it can only respond to known threats after they have been identified. This is in contrast to whitelisting software, which only allows approved applications to run, providing a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
Bypassing or Rendering Blacklisting Software Ineffective
Sophisticated cyber threats can bypass blacklisting software through techniques such as polymorphic malware, which constantly changes its code to evade detection. Attackers can also use encrypted communication channels to hide malicious activities from blacklists, making it difficult for the software to detect and block threats.
Furthermore, cybercriminals can exploit vulnerabilities in the blacklisting software itself to disable or bypass its protection mechanisms, rendering it ineffective in defending against attacks.
Best Practices for Implementing Blacklisting Software
Implementing blacklisting software is crucial for organizations to enhance their cybersecurity posture. Here are some best practices to consider:
Steps for Effective Implementation
- Define clear policies and guidelines: Establish specific rules for what should be blacklisted and communicate these clearly to all employees.
- Regularly update blacklists: Stay up-to-date with the latest threats and ensure that the blacklists are updated frequently to protect against new risks.
- Monitor and analyze traffic: Regularly monitor network traffic to identify any suspicious activity that may require blacklisting.
- Implement user training: Educate employees on the importance of following security protocols and the role of blacklisting software in protecting the organization.
Tips for Maintenance and Updates
- Automate updates: Use automated tools to regularly update blacklists and ensure that the software is always equipped to block new threats.
- Regular testing: Conduct regular testing to ensure that the blacklisting software is functioning correctly and effectively blocking malicious content.
- Review logs: Regularly review logs and reports generated by the blacklisting software to identify any patterns or trends that may indicate a need for adjustment.
Importance of Integration with Other Cybersecurity Measures
Integrating blacklisting software with other cybersecurity measures such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems is essential for comprehensive protection. By combining these tools, organizations can create multiple layers of defense against cyber threats and improve overall security.
Summary
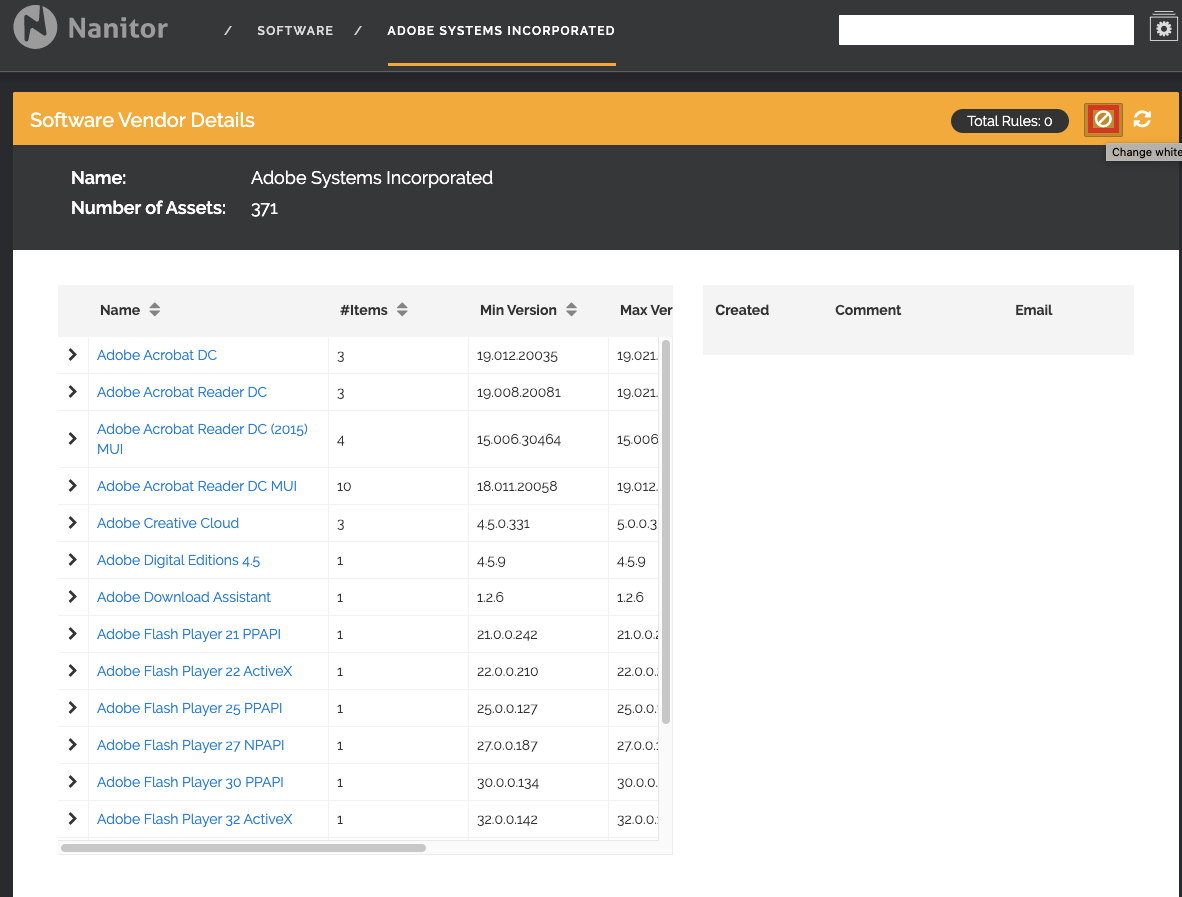
In conclusion, blacklisting software offers a robust defense against security threats when effectively implemented and integrated with other cybersecurity measures. Stay vigilant and proactive in safeguarding your digital assets.
FAQ Overview
How does blacklisting software differ from whitelisting software?
Blacklisting software blocks known threats based on a predefined list, while whitelisting software only allows approved entities to access systems or networks.
Can blacklisting software protect against zero-day attacks?
Blacklisting software may not be effective against zero-day attacks, which are new and unknown vulnerabilities. It’s crucial to complement it with other security measures.
Is blacklisting software suitable for small businesses?
Yes, blacklisting software can benefit small businesses by providing an added layer of security against common threats. However, tailored solutions may be necessary based on specific needs.
