Software blacklist is a crucial tool in cybersecurity, filtering out potential threats to protect systems. Let’s delve into its workings and importance.
Definition of Software Blacklist
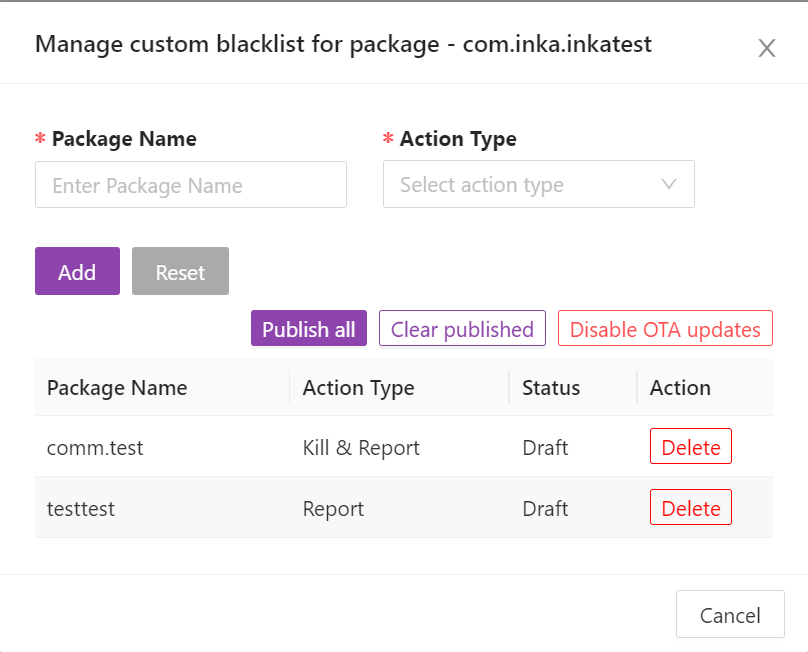
In the realm of cybersecurity, a software blacklist refers to a list of known malicious or unauthorized software applications that are prohibited from being installed or run on a system. This proactive approach helps organizations protect their networks and systems from potential security threats.
Common Types of Software Blacklists
- Hash-based Blacklists: These lists contain cryptographic hash values of known malware files, allowing for easy detection based on unique identifiers.
- Signature-based Blacklists: Signature patterns of known malware are stored in these lists to identify and block malicious software based on predefined patterns.
- Behavior-based Blacklists: These lists monitor software behavior for suspicious activities and block any program that exhibits malicious behavior.
Purpose of Using Software Blacklists in IT Security
Software blacklists play a crucial role in enhancing IT security by:
- Preventing malware infections: By blocking known malicious software, blacklists help prevent malware infections and data breaches.
- Enhancing system performance: By restricting the execution of unauthorized software, blacklists contribute to maintaining system performance and stability.
- Complying with security policies: Blacklists help organizations enforce security policies and regulations by prohibiting the use of unauthorized software.
How Software Blacklists Work
Software blacklists work by identifying and categorizing potentially harmful or unwanted software to prevent users from downloading, installing, or running them on their devices. These blacklists are crucial in maintaining cybersecurity and protecting users from malicious threats.
Adding Software to a Blacklist, Software blacklist
When adding software to a blacklist, security experts analyze the behavior, code, and reputation of the software. If the software is deemed malicious, unsafe, or unwanted, it is added to the blacklist to prevent users from accessing it.
Updating and Maintaining Blacklists
Software blacklists are regularly updated to include new threats and remove outdated entries. Security experts continuously monitor software behavior, security vulnerabilities, and emerging threats to ensure that the blacklist remains up-to-date and effective in protecting users.
Criteria for Blacklisting Software
- Presence of malware: Software containing malware or malicious code is immediately blacklisted to prevent harm to users.
- Security vulnerabilities: Software with known security vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals is added to the blacklist.
- Unwanted behavior: Software that engages in unauthorized activities, such as data collection without user consent, may be blacklisted.
- Poor reputation: Software with a history of security breaches, privacy violations, or unethical practices can also be blacklisted.
Impact of Software Blacklists

Running blacklisted software on a system can have serious consequences, affecting both individual users and organizations. It can lead to security vulnerabilities, data breaches, and system instability.
Preventing Security Breaches
Software blacklists play a crucial role in preventing security breaches by blocking known malicious programs from running on a system. By maintaining an updated blacklist, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access, data theft, and other cyber threats.
Protecting Networks from Malware
Software blacklists are essential in protecting networks from malware attacks. By blocking known malware-infected software, blacklists help maintain the integrity and security of the network infrastructure. This proactive approach can prevent the spread of malware and minimize the impact of potential cyber attacks.
Managing Software Blacklists
Effectively managing and implementing software blacklists is crucial for organizations to ensure the security and efficiency of their systems. However, it comes with its own set of challenges that need to be addressed. Here are some strategies, challenges, and best practices to optimize software blacklist policies:
Strategies for Effective Management
Implementing a software blacklist requires a well-thought-out strategy to ensure its effectiveness. Here are some key strategies:
- Regularly update the blacklist: Keep the list updated with the latest threats and vulnerabilities to provide adequate protection.
- Automate the process: Use automation tools to streamline the blacklist management process and ensure timely updates.
- Implement user education: Educate users on the importance of following the blacklist policies and the risks associated with unauthorized software.
- Monitor and enforce compliance: Regularly monitor system activities to ensure compliance with the blacklist policies and take appropriate actions against violations.
Challenges in Maintaining Software Blacklists
Maintaining a software blacklist can be challenging due to various factors. Some common challenges include:
- Keeping up with new threats: The constantly evolving threat landscape requires continuous monitoring and updating of the blacklist.
- User resistance: Users may resist following the blacklist policies, leading to potential security vulnerabilities.
- Compatibility issues: Blacklisted software may sometimes be required for specific tasks, creating compatibility challenges.
- Resource constraints: Limited resources may hinder the effective management and enforcement of the blacklist policies.
Best Practices for Optimizing Software Blacklist Policies
To optimize software blacklist policies, organizations can follow these best practices:
- Establish clear policies: Clearly define the rules and guidelines for software usage and communicate them effectively to all users.
- Regularly review and update policies: Periodically review and update the blacklist policies to adapt to changing security threats and organizational needs.
- Collaborate with IT and security teams: Work closely with IT and security teams to ensure alignment between the blacklist policies and overall security strategy.
- Provide training and support: Offer training programs and support resources to help users understand the importance of following the blacklist policies.
Summary

In conclusion, software blacklists play a vital role in safeguarding systems from malicious software, emphasizing the need for robust filtering measures in IT security.
FAQ Insights
How often should software blacklists be updated?
Software blacklists should ideally be updated regularly, at least weekly, to ensure they include the latest threats.
Can software blacklists completely eliminate security breaches?
While effective, software blacklists cannot guarantee complete elimination of security breaches but significantly reduce the risk.
